How Gas Fees Are Calculated in the Cryptocurrency Industry
In the world of cryptocurrency, gas fees play a crucial role in facilitating transactions and executing smart contracts. Understanding how these fees are calculated can empower users to make informed decisions when engaging with blockchain networks. This article delves into the intricacies of gas fees, their calculation methods, and the factors influencing their fluctuations.
What Are Gas Fees?
Gas fees are the costs associated with executing transactions or smart contracts on a blockchain network. They serve as an incentive for miners or validators to include a transaction in a block. Without gas fees, the network would struggle to function efficiently, as there would be no motivation for participants to process transactions.
How Gas Fees Are Calculated
The calculation of gas fees involves several components, primarily the gas limit and the gas price.
1. Gas Limit
The gas limit is the maximum amount of gas a user is willing to spend on a transaction. Each operation on the blockchain consumes a certain amount of gas, and the total gas used cannot exceed the gas limit set by the user. If the gas limit is too low, the transaction may fail, and the user will still incur a fee for the gas used up to that point.
2. Gas Price
The gas price is the amount a user is willing to pay per unit of gas, typically measured in Gwei (1 Gwei = 0.000000001 ETH). The gas price fluctuates based on network demand; during periods of high activity, users may need to increase their gas price to ensure their transactions are processed promptly.
3. Total Gas Fee Calculation
The total gas fee for a transaction can be calculated using the following formula:
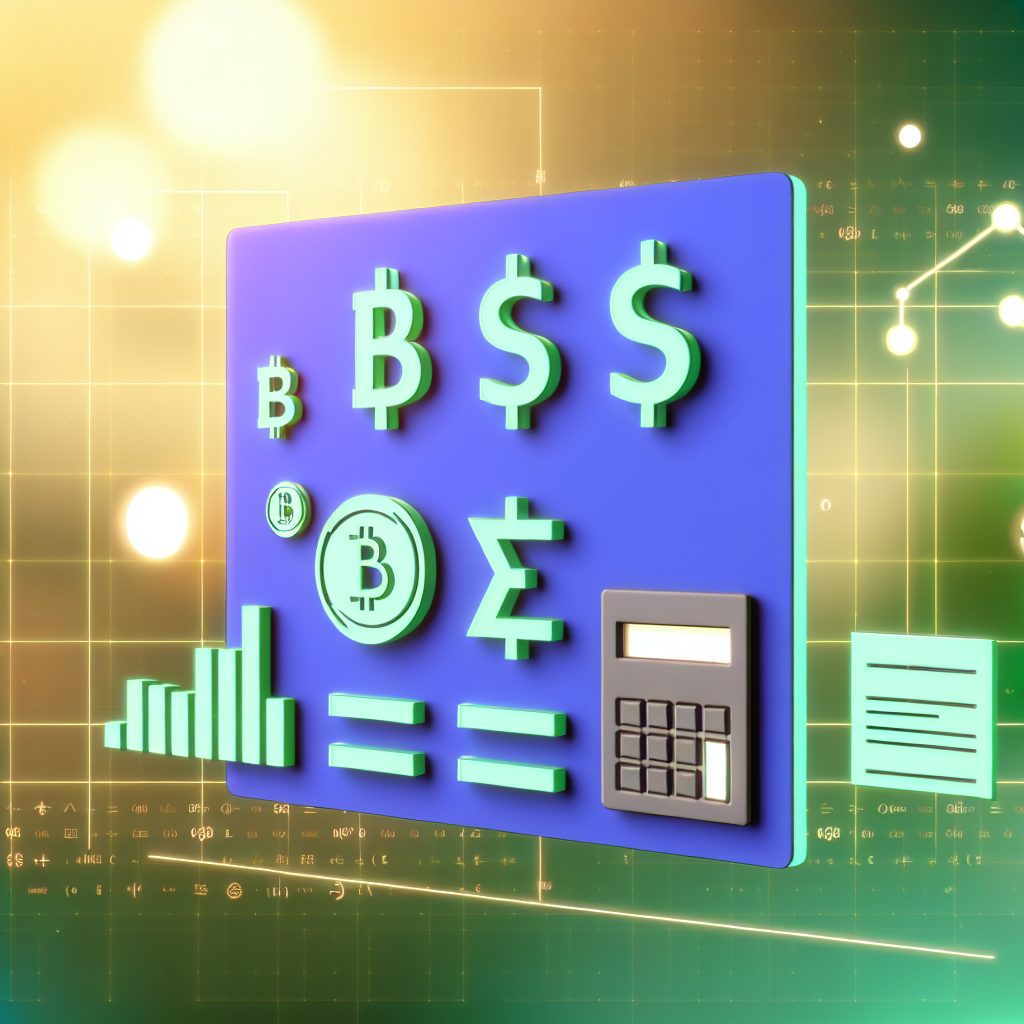

Total Gas Fee = Gas Limit x Gas Price
For example, if a user sets a gas limit of 21,000 units and a gas price of 100 Gwei, the total gas fee would be:
Total Gas Fee = 21,000 x 100 Gwei = 2,100,000 Gwei
To convert Gwei to ETH, divide by 1,000,000,000:
Total Gas Fee in ETH = 2,100,000 Gwei / 1,000,000,000 = 0.0021 ETH
Factors Influencing Gas Fees
Several factors can influence gas fees, including:
- Network Congestion: High transaction volumes can lead to increased gas prices as users compete to have their transactions processed.
- Transaction Complexity: More complex transactions, such as those involving smart contracts, require more gas, leading to higher fees.
- Market Conditions: The overall demand for Ethereum and other cryptocurrencies can impact gas prices.
- Time of Day: Gas prices can vary throughout the day based on user activity patterns.
Real-World Implications of Gas Fees
Gas fees can significantly impact users’ experiences on blockchain networks. For instance, during the DeFi boom in 2020, Ethereum gas fees skyrocketed, making it costly for users to execute transactions. This led to the emergence of layer-2 solutions and alternative blockchains that offer lower fees.
For example, the launch of Polygon (formerly Matic Network) provided a solution for users seeking lower transaction costs while still benefiting from Ethereum’s security. Polygon’s layer-2 scaling solution allows users to transact with significantly reduced gas fees, making it an attractive option for DeFi applications.
Strategies to Minimize Gas Fees
Users can adopt several strategies to minimize gas fees:
- Timing Transactions: Monitoring network congestion and executing transactions during off-peak hours can lead to lower gas prices.
- Setting Custom Gas Prices: Users can manually set gas prices based on current market conditions, allowing them to avoid overpaying.
- Using Layer-2 Solutions: Leveraging layer-2 networks like Polygon or Optimism can significantly reduce transaction costs.
- Batching Transactions: Combining multiple transactions into one can help save on gas fees.
Case Studies: Gas Fees in Action
To illustrate the impact of gas fees, consider the following case studies:
Case Study 1: Ethereum’s Gas Fee Surge in 2021
In May 2021, Ethereum experienced a massive surge in gas fees due to the popularity of NFTs and DeFi projects. Gas prices reached an all-time high, with average fees exceeding $70 per transaction. This surge prompted many users to seek alternatives, leading to increased interest in layer-2 solutions and other blockchains.
Case Study 2: The Rise of Binance Smart Chain
Binance Smart Chain (BSC) emerged as a popular alternative to Ethereum, offering significantly lower gas fees. During the DeFi boom, BSC attracted numerous projects and users looking for cost-effective solutions. The average gas fee on BSC was often less than $1, making it an appealing option for many.
Future of Gas Fees in Cryptocurrency
The future of gas fees in the cryptocurrency industry is likely to evolve as new technologies and solutions emerge. Ethereum’s transition to Ethereum 2.0 aims to address scalability issues and reduce gas fees through the implementation of proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus. Additionally, the growth of layer-2 solutions and alternative blockchains will continue to shape the landscape of transaction costs.
FAQs About Gas Fees
What is the average gas fee on Ethereum?
The average gas fee on Ethereum can vary significantly based on network activity. As of 2025, average fees typically range from $5 to $30, but they can spike during periods of high demand.
Can gas fees be refunded?
No, gas fees are non-refundable. If a transaction fails, the gas used up to that point is still charged to the user.
How can I check current gas prices?
Users can check current gas prices using various tools and websites, such as EthGasStation or GasNow.
Are gas fees the same across all blockchains?
No, gas fees vary across different blockchains. Each blockchain has its own fee structure and mechanisms for calculating transaction costs.
Conclusion
Understanding how gas fees are calculated is essential for anyone engaging with blockchain technology. By grasping the concepts of gas limits and gas prices, users can make informed decisions that optimize their transaction costs. As the cryptocurrency landscape continues to evolve, staying updated on gas fees and exploring alternative solutions will be crucial for maximizing efficiency and minimizing expenses.
For the latest news and updates in the cryptocurrency space, consider visiting Bitrabo. Follow me on social media for more insights: X, Instagram, and Threads.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. Always conduct your own research before making investment decisions.
The Crypto Watchlist of the Week 🔎
Subscribe to receive expert-curated projects with real potential—plus trends, risks, and insights that matter. Get handpicked crypto projects, deep analysis & market updates delivered to you.